English Period Furniture
The Evolution of English Furniture
Throughout the history of furniture, the changing styles have arrived by the conditions ruling at any one time. These conditions may have been the result of:
- The Limits of Knowledge, wood expansion and contraction
- The limits of equipment, only tools and saws
- The Availability of Timber, Local supply, only solid timber
- Economic Conditions, wealthy or not, changes
- Peace or War, determine furniture, immobile, security
- Overseas Influences, trade agreements, incentives
- Reigning Monarch
- A Movement
- A Generic influence
- A Religious Group
Britain had Oak and Beech as it’s native timber for furniture production, but with the discovery of new land and the establishment of overseas trade, other timber species suddenly became available:
Oak 1500-1600
Walnut 1660-1723
Mahogany 1715
Satinwood 1765
Prior to 1500, the Gothic Period, teaching and learning of craftsmanship was mostly overseen by the church. Therefore, most ornamentation on Gothic furniture follows the lines of ornamental stonework from the Gothic Churches and buildings.
The carpenter, blacksmith and the turner made the furniture. It consisted of tables, forms, stools and chests. The chest was the principal piece as it served not only as storage, but also a seat or table. Tables generally were loose boards on top of trestles.
Henry VII, came to the throne following the war of the roses in 1485, and was the first Tudor monarch. During this time Britain had found peace and order not previously known.
Henry VIII succeeded his father in 1509, and inherited his accumulated treasures. He continued to change the Gothic style by keeping up his father’s interest in foreign artists and craftsmen. More economical printing materials were available which allowed for pattern books from the continent.
The wealth of the country increased under the stable Tudor government and a new middle class was formed creating a demand for a new form of furniture.
Therefore the 16th Century can be divided into two halves. The first part, furniture consisted of carving on gothic framework, stools and forms were the only form of seating available.
The second part, new pieces of furniture evolved. Buffets or sideboards, fold top games tables, taller chests which doors became cupboards or hutches and the draw leaf table which is still common today.

A simple timber planked chest
Chairs were developed from chests and had upright back legs, heavy turning and often carved panels.
Tudor Gothic Furniture Characteristics
Plank Chest – Simple Plank construction by a carpenter and blacksmith. Metal straps and nails were used to hold the timber together but because of the arrangement of grain the timber often split. They often had handles to carry it.
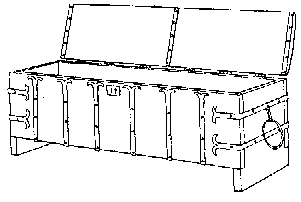
A simple timber planked chest
Chest / Partly Framed Chest – This was superseded by the partly framed chest. It used dry pegged construction and panel fitted into the frame allowed for movement without the timber splitting. Panels from riven boards were hand moulded and sometimes carved to give the “linenfold” effect. The board is cut with a wedge and split.
Built In Seating – Early settles accommodated up to six people with simple linenfold panels and foot rest rail.
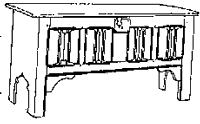
Joined or Joyned Chest c1530
Wainscott panelwork was used on the walls.
Joined Chest – Joyned or joined distinguished the work of the joiners from the carpenter.
Settles – Settles were made more movable. The seat had a lift up lid for storage. The arm supports were shaped for added comfort. Some were adaptable into tables as well as seats.
Credence – A table to hold bread and wine for holy Communion. Panels carved with bunches of grapes and vines. They often had an overhead canopy.

Carved linen fold panel
More information on Styles and Periods of Interior Decorating
Styles and Periods
Furniture History
Decorating Styles
Period Decoration
What is Style?
